2015 Multiple Choice
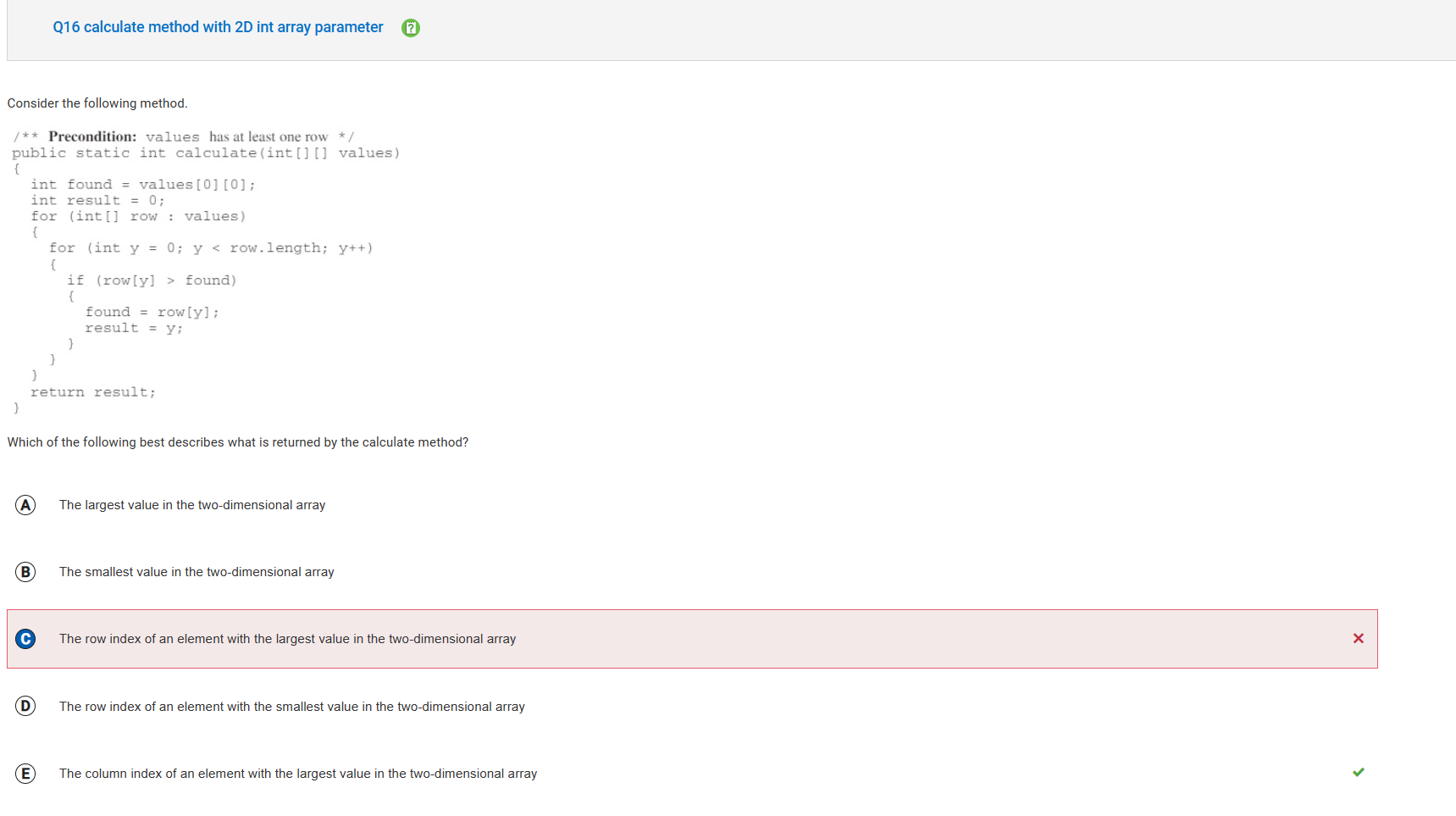
- Because the algorithm uses a for-each loop to traverse the rows, the row index is not being stored.
- Prior to the start of the nested for loops, the value of found is initialized to the element at row 0, column 0 in values and result is initialized to 0.The outer for loop iterates across all rows in values. The inner for loop iterates across the column indices of each row. When an element is located in the two-dimensional array that is larger than the current value stored in found, then this value is assigned to found and the column index is assigned to result. When the nested loop structure stops executing, the largest element in values is stored in found and the column in which that element was located is stored in result.
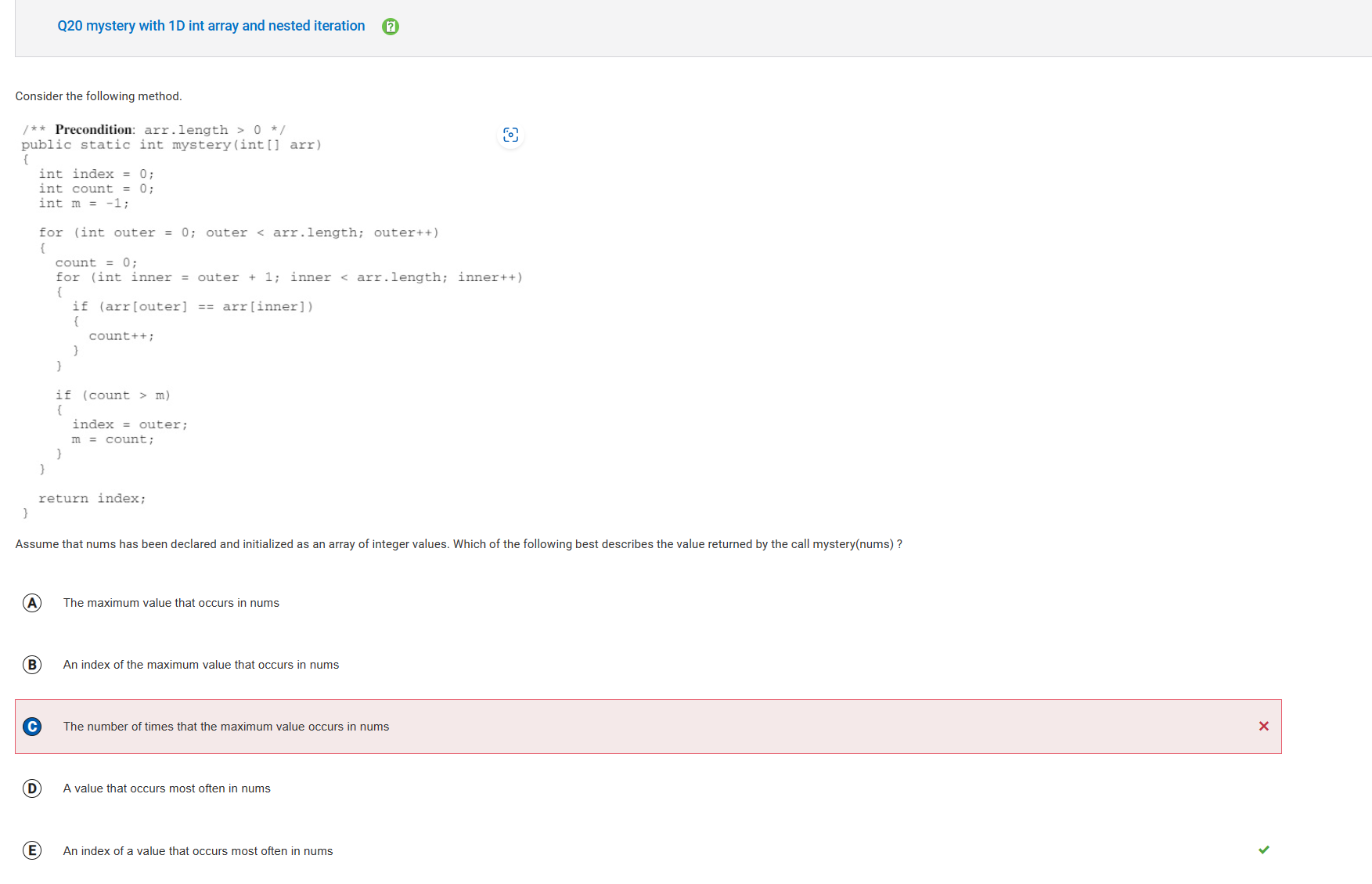
- The outer loop starts at 0 and loops through all the indices in arr. The inner loop starts at the index that is one more than outer and iterates through all indices to the right of this element. For each iteration of the inner loop, the element at the current value of outer is compared with each subsequent element. If the elements are equal, then count is incremented. This results in counting the number of occurrences of each value in the arr. After the inner loop terminates, if the number of occurrences of the current value is greater than previous highest count, the new count is assigned to m and the index of this element is stored in index. The method then returns the value of index, which represents the index of a value that occurs most often in nums.
- I confused the maximum number with occuring the most times aka maximum count of numbers
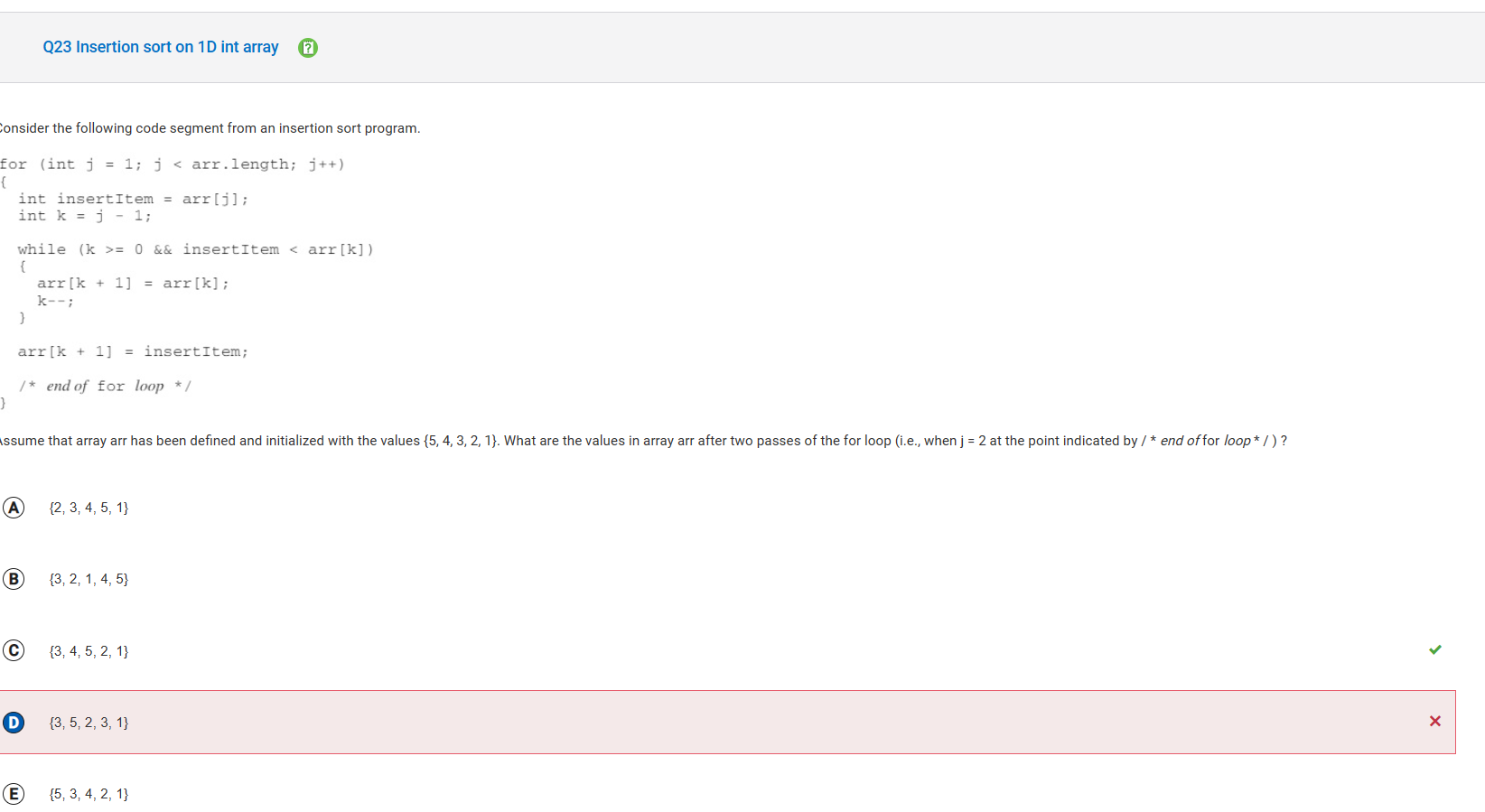
- In the first pass of the loop, arr[1] is assigned the value insertItem, which is 4 and k is assigned the value 0. The boolean expression in the while loop is true, since k is equal to 0 and 4 is less than arr[0], which is 5. In the body of the for loop arr[1] is assigned the value of arr[0], making the array have the contents {5, 5, 3, 2, 1} and k is decremented by 1, making it -1. The while loop boolean expression is now false and arr[0] is assigned the value of insertItem, which is 4. The array arr has the contents {4, 5, 3, 2, 1} after the first pass. The second pass, when j = 2, arr[2] is assigned insertItem, which is 3, and k is assigned 1. The boolean expression in the while loop is true, so arr becomes {4, 5, 5, 2, 1} and k is assigned 0. The boolean expression in the while loop is true, so arr becomes {4, 4, 5, 2, 1} and k is assigned -1. The boolean expression is now false and arr becomes {3, 4, 5, 2, 1} at the end of two passes through the for loop.
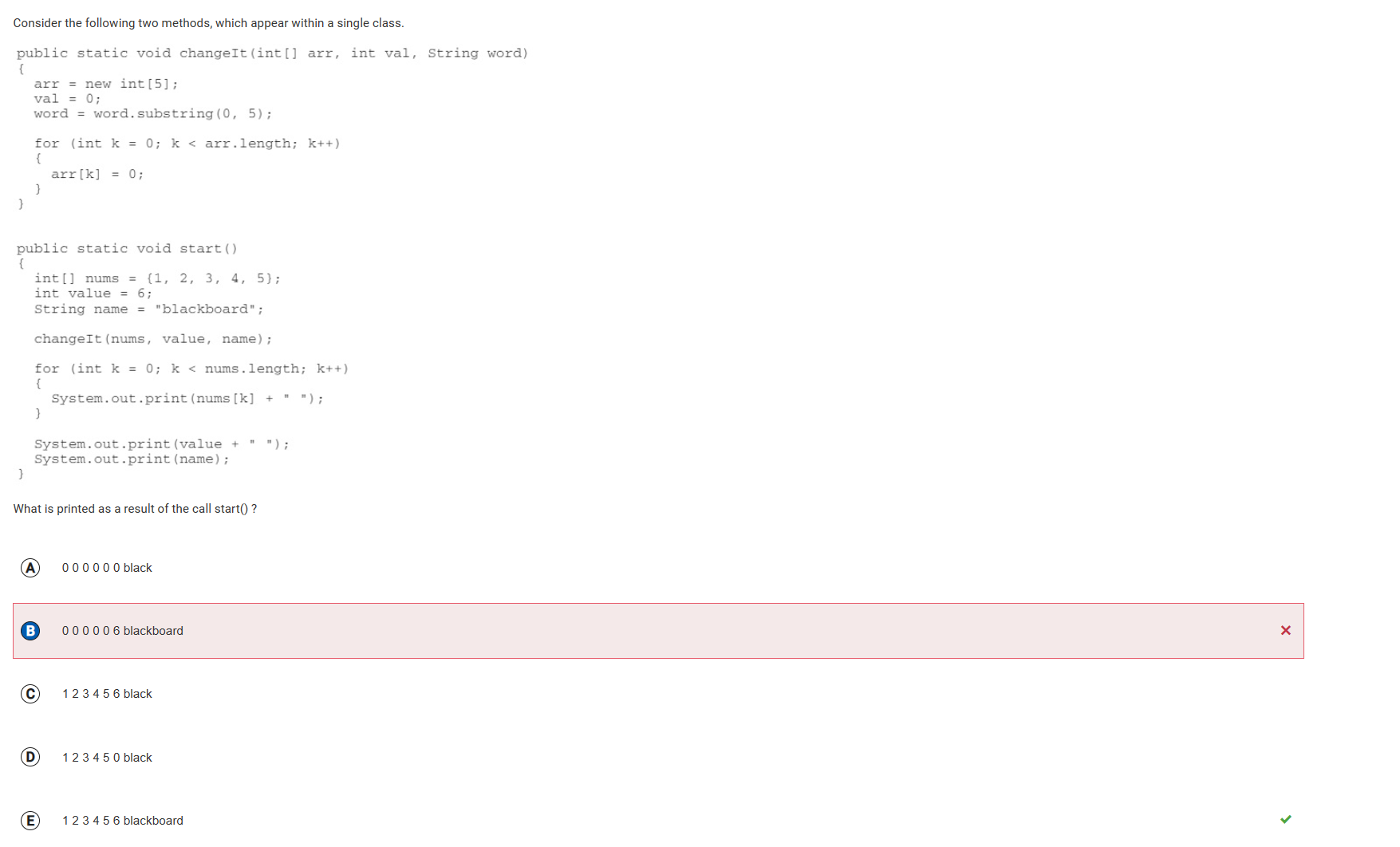
- . Parameters are passed using call by value. Call by value initializes the formal parameters (arr, val, word) with copies of the actual parameters (nums, value, name). When the parameter is a reference variable, the method receives a reference and can mutate the object being referenced but cannot alter the reference itself. Passing an object reference as a parameter will result in the formal parameter and the actual parameter being aliases. They both refer to the same object. When we call changeIt and pass the objects num and name, the formal parameters arr and word will reference these same objects. A copy of the object is not made. However, the first part of the method assigns new objects to arr and word, which means that any changes made to arr and word do not affect the actual parameters num and name. They remain unchanged. Updating val to 0 will not affect value. Therefore, the original values for num, value and name are printed.
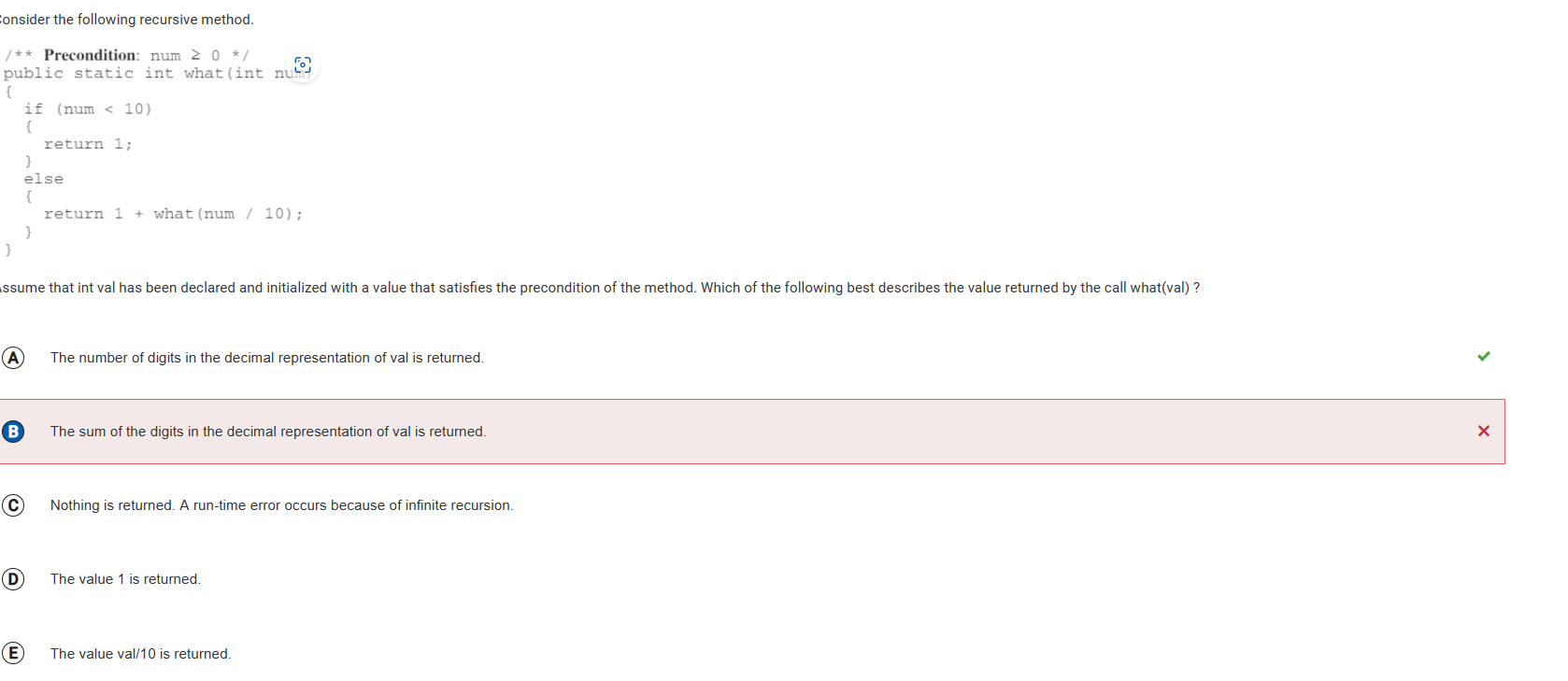
Each recursive call is made with the value num / 10. The expression num / 10 uses integer division and evaluates to an integer that is num with the right most digit removed. For example, 258 / 10 = 25. Each time the recursive call is made, what is returned is 1 plus the result of the recursive call. For example, what(258) = 1 + what(25) and what(25) = 1 + what(2) and what(2) = 1. Therefore what(258) = 1 + 1 + 1 or 3, which is the number of digits in 258.
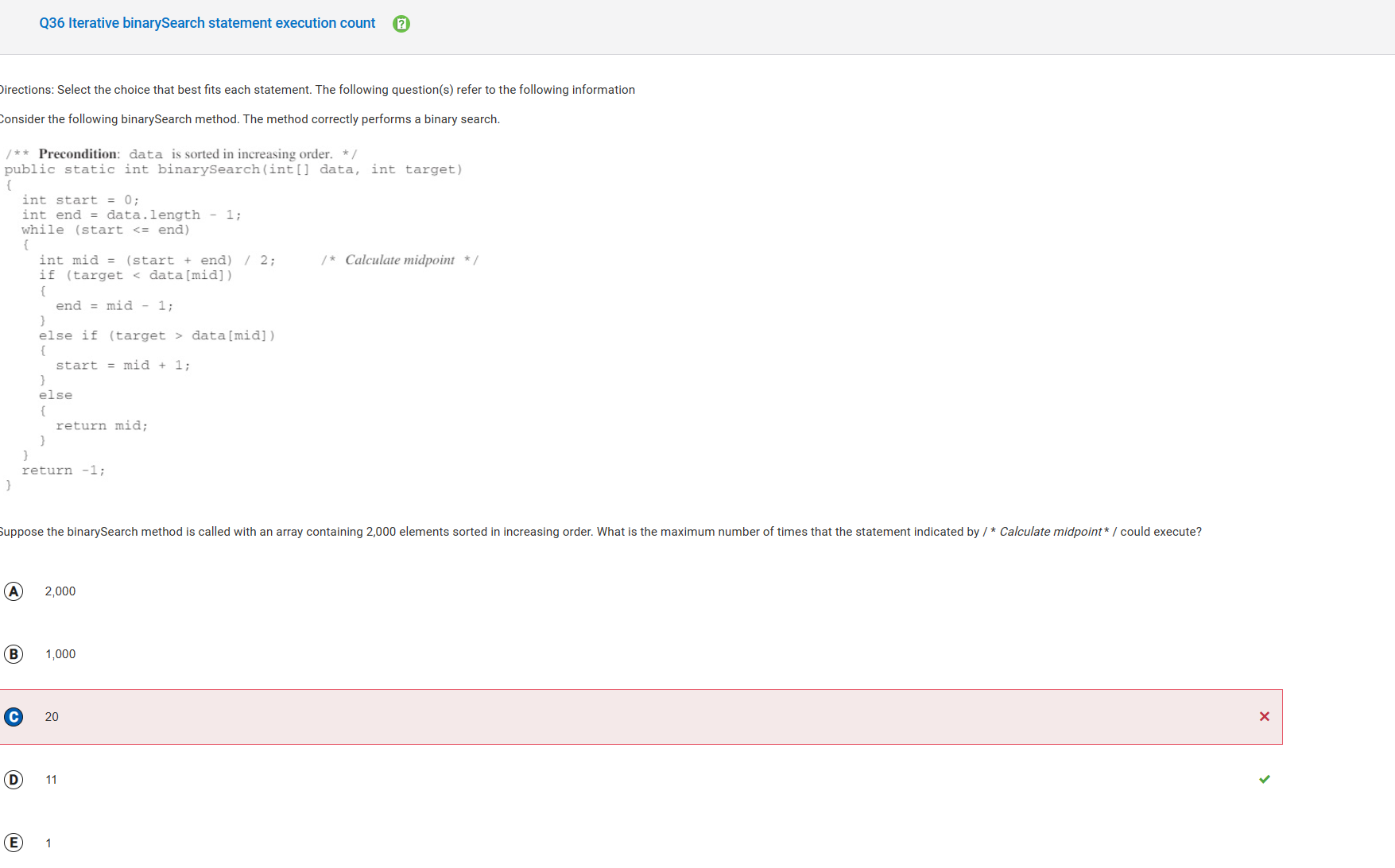
- The first iteration would check the middle element of 2000 and eliminate approximately 1000 elements. The second iteration would check the middle element of 1000 and eliminate approximately 500 elements. The third would eliminate approximately 250 elements. The fourth would eliminate approximately 125 elements. The fifth would eliminate approximately 62 elements. The sixth would eliminate approximately 31 elements. The seventh would eliminate approximately 15 elements. The eighth would eliminate approximately 7 elements. The nineth would eliminate approximately 3 elements. The tenth would eliminate approximately 1 element. The eleventh iteration would be the final iteration to determine if the element was found or not.